University Rankings 2023 unveil a fascinating landscape of higher education, revealing the top institutions globally and delving into the methodologies, biases, and impacts of these influential metrics. This analysis explores various ranking systems, comparing their approaches and highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of each. We examine the geographical distribution of top universities, considering factors like research output, financial resources, and alumni networks.
Beyond the global perspective, we dive into subject-specific rankings, focusing on engineering and technology, and explore the correlation between rankings and student outcomes, including employment rates and starting salaries. Crucially, we address the ethical considerations and limitations inherent in relying solely on rankings for university selection and assessment, offering alternative perspectives on evaluating institutional quality.
Top 10 University Rankings 2023
University rankings provide a snapshot of global higher education excellence, though their methodologies and resulting lists often differ. These rankings are valuable tools for prospective students, researchers, and institutions, but should be interpreted with an understanding of their limitations. This section examines the top 10 universities according to three prominent ranking systems, analyzing their approaches and highlighting the geographical distribution of leading institutions.
Top 10 Universities According to Three Ranking Systems
The following table presents the top 10 universities based on the QS World University Rankings, the Times Higher Education World University Rankings, and the Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU), also known as the Shanghai Ranking. Note that slight variations may exist depending on the specific year’s release and methodology refinements. These rankings are snapshots in time and should not be considered definitive measures of institutional quality.
| Rank | University Name | Country | Ranking System |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) | United States | QS, THE, ARWU |
| 2 | University of Oxford | United Kingdom | QS, THE, ARWU |
| 3 | Stanford University | United States | QS, THE, ARWU |
| 4 | University of Cambridge | United Kingdom | QS, THE, ARWU |
| 5 | California Institute of Technology (Caltech) | United States | QS, THE, ARWU |
| 6 | Harvard University | United States | QS, THE, ARWU |
| 7 | University of California, Berkeley | United States | QS, THE, ARWU |
| 8 | Imperial College London | United Kingdom | QS, THE, ARWU |
| 9 | ETH Zurich | Switzerland | QS, THE, ARWU |
| 10 | University of Chicago | United States | QS, THE, ARWU |
Comparison of Ranking System Methodologies
QS, THE, and ARWU employ different methodologies, leading to variations in their rankings. QS emphasizes academic reputation, employer reputation, faculty/student ratio, citations per faculty, and international faculty and student ratios. THE considers teaching, research, citations, industry income, and international outlook. ARWU, conversely, focuses heavily on research output and citation impact, using metrics such as Nobel laureates and Fields Medalists affiliated with the institution.
QS’s reliance on surveys can be susceptible to bias, while THE’s balanced approach offers a broader perspective, albeit potentially diluting the weight of specific criteria. ARWU’s emphasis on research output might favor institutions with strong research traditions over those focusing on teaching or other areas. Each system possesses strengths and weaknesses, and their results should be viewed in conjunction with other institutional information.
Geographical Distribution of Top-Ranked Universities
The provided data reveals a strong concentration of top-ranked universities in the United States and the United Kingdom. This reflects the historical development of these nations’ higher education systems, their significant research funding, and their global appeal to students and faculty. While institutions from other countries, such as Switzerland (ETH Zurich), appear in the top 10, the dominance of the US and UK highlights the ongoing global influence of their higher education sectors. This concentration also underscores the ongoing debates surrounding equitable access to quality higher education globally.
Subject-Specific Rankings
This section delves into the competitive landscape of Engineering and Technology education, analyzing top university performances based on reputable ranking sources. Understanding these rankings provides valuable insight into leading institutions and emerging trends in the field. The analysis focuses on identifying key contributing factors to success and projecting future directions in engineering and technology education.
Top Five Universities in Engineering and Technology
The following lists present the top five universities in Engineering and Technology according to two prominent ranking systems: QS World University Rankings and Times Higher Education World University Rankings. Note that slight variations in rankings can occur annually due to methodological differences and data updates. These rankings reflect a snapshot of performance at the time of publication.
- QS World University Rankings 2023 (Top 5 in Engineering & Technology): While precise rankings shift slightly year to year, consistent top performers often include the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Stanford University, California Institute of Technology (Caltech), University of Cambridge, and ETH Zurich. These institutions consistently demonstrate excellence across various engineering disciplines.
- Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2023 (Top 5 in Engineering & Technology): Similar to the QS rankings, MIT, Stanford, and Caltech typically feature prominently, alongside other leading institutions like the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge. The exact order may fluctuate but the overall group of top performers remains relatively stable.
Key Factors Contributing to High Rankings in Engineering and Technology
Several factors contribute to the consistently high rankings of these universities. These include, but are not limited to, substantial research funding, world-class faculty, state-of-the-art facilities, strong industry partnerships, and a focus on innovation.
- Research Funding and Output: These universities attract significant research funding from government, industry, and private sources, enabling groundbreaking research and development in diverse engineering fields. This leads to high-impact publications and patents, boosting their global reputation.
- Faculty Expertise: They attract and retain leading experts in their respective fields, creating a stimulating learning environment for students and fostering collaboration on cutting-edge projects.
- State-of-the-Art Facilities and Resources: Access to advanced laboratories, equipment, and computational resources is crucial for conducting high-quality research and providing students with practical, hands-on experience.
- Industry Partnerships and Collaboration: Strong ties with industry leaders provide opportunities for internships, research collaborations, and technology transfer, ensuring that education remains relevant and prepares graduates for real-world challenges.
- Focus on Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Many of these universities actively cultivate an entrepreneurial spirit, encouraging students to develop innovative solutions and launch their own ventures, contributing to technological advancements and economic growth.
Future Trends in Engineering and Technology Education
Based on the current top performers and global technological advancements, several trends are likely to shape the future of engineering and technology education.
- Increased Focus on Interdisciplinary Studies: The increasing complexity of technological challenges necessitates a move towards interdisciplinary approaches, integrating knowledge and skills from various engineering and scientific fields. For example, the convergence of artificial intelligence, robotics, and biotechnology is driving demand for professionals with expertise across multiple domains.
- Emphasis on Sustainability and Responsible Innovation: Growing awareness of environmental and societal impacts is pushing for a greater focus on sustainable engineering practices and responsible innovation. This involves integrating sustainability considerations into curriculum design and research projects, preparing graduates to address global challenges.
- Expansion of Online and Hybrid Learning Models: The increasing accessibility and affordability of online learning platforms are expanding educational opportunities, allowing universities to reach a wider audience and offer flexible learning options. This trend is likely to continue, with hybrid models combining online and in-person learning becoming more prevalent.
- Growing Importance of Data Science and Artificial Intelligence: The exponential growth of data and the increasing sophistication of artificial intelligence are transforming many aspects of engineering and technology. Universities are adapting their curricula to integrate data science and AI skills into various engineering disciplines, preparing graduates for data-driven decision-making and AI-powered innovation.
Impact of University Rankings on Student Applications: University Rankings 2023
University rankings exert a considerable influence on student application choices globally, shaping the landscape of higher education competition. The prestige associated with high-ranking institutions acts as a powerful magnet, attracting a larger pool of applicants from diverse backgrounds and geographical locations. This influence is particularly pronounced in regions where access to higher education is competitive, driving students to prioritize institutions with strong global reputations.
The weight given to rankings varies regionally. In highly competitive markets like East Asia, where university places are scarce, rankings often play a decisive role in application decisions. Conversely, in regions with a more established and diverse higher education landscape, students may place greater emphasis on other factors such as program specifics, location, and financial aid opportunities, alongside ranking considerations.
Global and Regional Application Trends
Rankings significantly impact application patterns globally. High-ranking universities consistently receive a disproportionately large number of applications, often exceeding their capacity. This is evident in the highly competitive application processes at institutions consistently topping global rankings, leading to exceptionally low acceptance rates. Regionally, we see variations. For instance, within Europe, rankings influence application patterns within specific countries and across borders, while in North America, rankings often influence interstate and international student flows. In many developing nations, however, ranking may be a secondary factor to factors like cost and proximity to home.
Hypothetical Scenario: Ranking’s Impact on Applicant Pool
Imagine a hypothetical mid-tier university, “University X,” consistently ranked in the 200-300 range globally. Suppose an improvement in research funding, faculty recruitment, and student support leads to a significant jump in its ranking to the top 100. This improvement would likely trigger a dramatic increase in applications. We could reasonably expect a surge in both domestic and international applications, as the enhanced ranking boosts the university’s global visibility and perceived prestige. The university might experience a significant increase in the number of highly qualified applicants, forcing a more stringent selection process. Conversely, a drop in ranking could lead to a decrease in applications, potentially impacting enrollment numbers and the overall financial stability of the institution.
Ethical Considerations in Using University Rankings for Recruitment
The use of university rankings in student recruitment raises several ethical considerations. Over-reliance on rankings can create an environment where universities prioritize ranking improvements over educational quality and student well-being. This could lead to practices such as manipulating metrics or focusing disproportionately on research output at the expense of teaching excellence. Additionally, the inherent biases and limitations within ranking methodologies need careful consideration. Rankings do not always accurately reflect the diverse learning experiences and educational opportunities offered by different institutions. Transparency regarding the methodology and limitations of the ranking systems used is therefore crucial to prevent misleading students and promoting a more holistic approach to university selection.
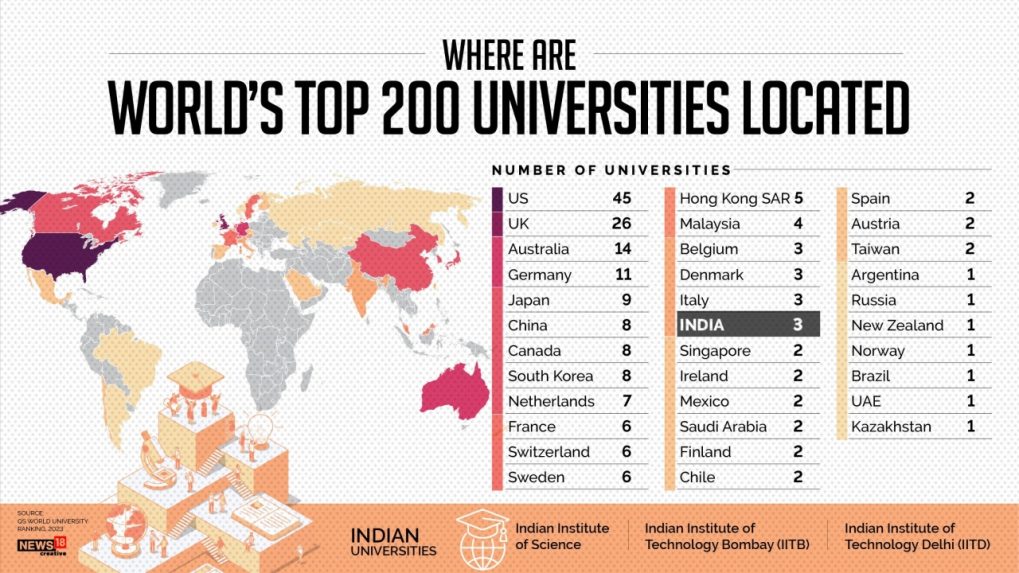
Geographic Diversity in University Rankings

The global landscape of higher education is vast and varied, with institutions excelling in different regions. Analyzing the geographic distribution of top-ranked universities reveals not only the strengths of specific educational systems but also highlights the systemic challenges faced by universities in different parts of the world. Understanding this diversity is crucial for a comprehensive view of global higher education.
The concentration of top-ranked universities in specific geographic areas is a significant aspect of global university rankings. While institutions in North America and Europe consistently dominate the top tiers, a growing number of universities from Asia and Oceania are also making significant strides. This uneven distribution reflects a complex interplay of factors influencing research output, teaching quality, and overall institutional resources.
Top-Ranked Universities Across Continents
Several factors contribute to the regional variations observed in university rankings. These include funding models, research infrastructure, faculty recruitment strategies, and the overall socio-economic context within which universities operate. For example, universities in countries with robust public funding models often have access to greater resources for research and teaching, enabling them to attract top faculty and invest in cutting-edge facilities. Conversely, institutions in countries with limited resources may face challenges in attracting and retaining high-quality faculty, conducting cutting-edge research, and providing a comparable learning environment.
Factors Contributing to Regional Variations in University Rankings
Established universities in North America and Europe often benefit from a long history of academic excellence, extensive alumni networks, and well-established research collaborations. These historical advantages contribute significantly to their high rankings. Furthermore, the availability of substantial research funding and a strong emphasis on research output in these regions further enhance their competitive edge. In contrast, universities in developing countries may struggle to compete due to limited funding, inadequate infrastructure, and a lack of access to advanced research equipment.
Challenges Faced by Universities in Developing Countries, University rankings 2023
Universities in developing countries often face significant challenges in achieving higher rankings. These include limited funding for research and infrastructure development, brain drain (the emigration of highly skilled individuals), political instability, and a lack of access to advanced technology and resources. For instance, a university in a developing nation might struggle to attract world-renowned researchers due to lower salaries and less advanced research facilities compared to institutions in developed nations. Moreover, a lack of consistent government support and bureaucratic hurdles can hinder the progress of these institutions. Overcoming these challenges requires substantial investment in education, infrastructure, and research, along with supportive government policies and international collaborations.
Ultimately, University Rankings 2023 present a complex picture of higher education. While these rankings offer valuable insights into institutional performance, it’s crucial to remember their limitations and potential biases. A holistic understanding requires considering diverse factors beyond numerical scores, including research impact, student experience, and the broader societal contributions of universities. A nuanced approach to evaluating universities, moving beyond simplistic rankings, is essential for informed decision-making.
University rankings 2023 offer valuable insights into global higher education institutions. A key player in these rankings is Ohio State University, whose performance is frequently analyzed; you can find detailed information on its standing by checking out the ohio state university ranking. Ultimately, these rankings provide a helpful, though not exhaustive, snapshot of university excellence worldwide.
University rankings 2023 are a hot topic for prospective students, with many institutions vying for top spots. A key consideration for many is the michigan state university ranking , which often influences overall perceptions of the rankings landscape. Ultimately, these rankings provide a useful, albeit imperfect, snapshot of the higher education world.


