American University Ranking: Navigating the complex landscape of higher education in the United States requires understanding the various ranking systems and their methodologies. This guide delves into the intricacies of national, regional, and specialized rankings, exploring the factors that contribute to a university’s overall standing and providing insights into the strengths and weaknesses of different ranking methodologies. We’ll examine not only academic rigor but also crucial aspects like student life, financial aid, career outcomes, and the increasingly important role of internationalization in shaping a university’s reputation.
From analyzing the top universities based on established ranking systems like US News & World Report to exploring the nuances of regional variations and subject-specific excellence, this guide offers a multifaceted perspective on American university rankings. We will also investigate the often-overlooked aspects of campus culture, financial accessibility, and the long-term impact of alumni networks and research output on a university’s overall success and prestige. The aim is to provide a balanced and informative resource for prospective students, current students, and anyone interested in understanding the complexities of the American higher education system.
Factors Influencing Rankings

University rankings, while often debated, significantly impact a university’s reputation, attracting prospective students and faculty, and securing research funding. Several key factors contribute to these rankings, with academic rigor and available resources playing a particularly crucial role. Understanding these factors allows universities to strategically improve their standing.
The weight given to academic rigor and resource allocation varies across different ranking organizations like US News & World Report, Times Higher Education, and QS World University Rankings. While all consider these elements, their methodologies differ in the specific metrics employed and the emphasis placed on each. This variation reflects differing philosophies on what constitutes a “good” university.
Faculty Resources
Faculty quality is a cornerstone of any university’s reputation. Ranking organizations assess this through various metrics, including the faculty’s publication record in high-impact journals, the number of prestigious awards and grants received by faculty members, and the overall reputation of the faculty within their respective fields. A higher proportion of full professors compared to adjunct faculty generally indicates a more established and experienced teaching staff, positively impacting a university’s ranking. For instance, a university with a high percentage of faculty members who are fellows of prestigious academies or have won Nobel Prizes will score higher in this category than one with a largely untenured faculty.
Student-to-Faculty Ratio
A lower student-to-faculty ratio often indicates smaller class sizes and more individualized attention for students. This is generally viewed favorably by ranking organizations as it suggests a more conducive learning environment and greater opportunities for interaction between students and professors. A university with a ratio of 10:1 (10 students per faculty member) would generally rank higher than one with a ratio of 20:1, all other factors being equal. This metric reflects the level of personalized teaching and mentorship available.
Research Funding
Research funding is a crucial indicator of a university’s research capabilities and its ability to attract top researchers. Ranking organizations often consider the total amount of research funding received by the university, the sources of this funding (e.g., government grants, private donations, industry partnerships), and the success rate of grant applications. A university securing substantial funding from prestigious organizations like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) or the National Science Foundation (NSF) would demonstrate strong research capabilities, positively influencing its ranking. For example, a substantial increase in NIH funding could significantly boost a university’s ranking within the life sciences. Similarly, securing large endowments for specific research areas could improve overall rankings.
Financial Aid and Affordability
The cost of higher education is a significant barrier for many aspiring students, making financial aid and affordability crucial factors in choosing a university. Access to financial aid not only impacts individual students’ ability to pursue higher education but also influences the diversity and socioeconomic representation within universities. Understanding the financial aid landscape at different institutions is essential for prospective students and their families.
Affordability, while intrinsically linked to financial aid, extends beyond just the availability of aid packages. It encompasses factors such as tuition fees, living expenses, and the overall cost of attendance. The relationship between affordability and university rankings is complex, with highly ranked institutions often having higher tuition costs, potentially offset by more generous financial aid offerings. This necessitates a careful examination of the net price – the actual cost a student and their family will pay after factoring in grants, scholarships, and loans.
Comparison of Financial Aid Packages at Six Highly-Ranked Universities
The following comparison highlights the financial aid packages offered by three highly-ranked public and three highly-ranked private universities. It’s important to note that these are general observations and individual aid packages vary significantly based on factors such as student need, merit, and academic achievement. Data is based on publicly available information from the respective universities’ websites and should be considered as a snapshot in time, subject to change.
American university rankings are a complex and often debated topic, with various methodologies employed. Understanding where a university stands within this landscape is crucial for prospective students. A prime example is Arizona State University Tempe, whose ranking you can explore in detail at arizona state university tempe ranking. Ultimately, these rankings offer just one perspective in the broader context of American higher education.
- Public Universities:
- University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley): UC Berkeley offers a comprehensive financial aid program including grants, loans, and work-study opportunities. Their aid packages often cover a significant portion of tuition and fees for eligible students, with a strong emphasis on need-based aid. They also have robust scholarship programs for high-achieving students.
- University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (UMich): Similar to UC Berkeley, UMich provides a mix of need-based and merit-based aid. Their aid programs often involve a combination of federal and institutional grants, loans, and work-study positions. The university also boasts a substantial endowment which contributes to its financial aid resources.
- University of Virginia (UVA): UVA’s financial aid program is largely need-based, aiming to make the university accessible to students from all socioeconomic backgrounds. Their commitment to need-blind admissions ensures that financial need does not affect the admissions process, although financial aid is determined after admission.
- Private Universities:
- Stanford University: Stanford is known for its generous financial aid program, which is need-blind and aims to meet 100% of demonstrated financial need for all admitted students. Their financial aid packages often include substantial grants and scholarships, minimizing the need for student loans.
- Yale University: Similar to Stanford, Yale offers a need-blind admissions policy and meets the full demonstrated financial need of admitted students. Their financial aid program is comprehensive and designed to ensure affordability for students from all backgrounds.
- Princeton University: Princeton also adopts a need-blind admissions policy and commits to meeting 100% of demonstrated financial need for all admitted students. Their financial aid program is highly generous and includes a significant grant component.
The Relationship Between Affordability and University Rankings
While high rankings often correlate with high tuition costs, the relationship between affordability and rankings is not strictly linear. Many highly-ranked universities, particularly private institutions, offset high tuition costs with generous financial aid programs. The net price, after considering financial aid, can be significantly lower than the sticker price. However, less affluent students may still face significant challenges accessing even the most generous aid packages due to complexities in the application process or a lack of awareness of available resources. The perception of affordability is also influenced by factors such as the availability of scholarships and grants, the prevalence of loan programs, and the overall cost of living in the university’s location.
Recommendations for Improving Accessibility for Students from Diverse Socioeconomic Backgrounds
Universities can significantly improve accessibility for students from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds through several key strategies.
American university rankings are a complex landscape, with various methodologies influencing the final results. Understanding these rankings requires careful consideration of the factors involved. A key institution within this system is the University of Georgia, whose standing you can explore further via this helpful resource: university of georgia ranking. Ultimately, these individual university rankings contribute to the broader picture of American higher education excellence.
- Increase need-based financial aid: Expanding need-based financial aid programs and ensuring that these programs cover a greater percentage of the total cost of attendance is crucial.
- Simplify the financial aid application process: Streamlining the application process and providing clear, accessible information about financial aid options can significantly improve accessibility for students and families who may be unfamiliar with the complexities of the system.
- Expand merit-based scholarships: Offering a wider range of merit-based scholarships can attract high-achieving students from all socioeconomic backgrounds, further diversifying the student body.
- Provide comprehensive financial literacy programs: Educating students and families about financial aid options, budgeting, and responsible borrowing can empower them to make informed decisions about financing their education.
- Increase transparency in pricing and financial aid information: Making the cost of attendance and financial aid information readily available and easy to understand can help students make informed choices about their higher education options.
Alumni Network and Career Outcomes
A strong alumni network and successful career placement are increasingly important factors for prospective students when evaluating universities. The value extends beyond simply securing a high-paying job immediately after graduation; it encompasses long-term career trajectory, professional development opportunities, and a sense of community that lasts a lifetime. This section examines the crucial role alumni networks play in post-graduation success and explores how universities can enhance these networks to better support their graduates.
The strength of a university’s alumni network is directly correlated with the career success of its graduates. A robust network provides access to mentorship, job opportunities, and valuable industry insights, all of which contribute to higher starting salaries and improved career placement rates. This, in turn, enhances the university’s reputation and attracts even more high-achieving students, creating a positive feedback loop.
Average Starting Salaries and Career Placement Rates
The following table compares average starting salaries and career placement rates for graduates of three highly-ranked universities. Note that these figures can vary depending on the specific major and year of graduation, and data may be sourced from different surveys and self-reporting methods. Therefore, it is crucial to consult multiple sources for a comprehensive understanding. The data presented below is illustrative and should be treated as an example.
| University | Average Starting Salary (USD) | Career Placement Rate (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| University A | 75,000 | 92 | Data based on a 2023 survey of graduates from the business school. |
| University B | 70,000 | 88 | Data based on a 2022 self-reported survey of graduates. |
| University C | 68,000 | 85 | Data compiled from various sources, including university reports and third-party surveys. |
The Role of Alumni Networks in Career Success
Alumni networks act as invaluable resources for graduates navigating the complexities of the job market. Mentorship opportunities, provided by established professionals within the network, offer guidance on career paths, skill development, and networking strategies. Access to exclusive job postings and internship opportunities, often shared within the alumni community, significantly improves graduates’ chances of securing employment aligned with their career goals. Furthermore, the social and emotional support provided by a strong alumni network can mitigate the stress and uncertainty associated with the transition from academia to the professional world.
Strengthening Alumni Networks to Improve Career Outcomes, American university ranking
Universities can proactively enhance their alumni networks to better serve their graduates. This involves implementing strategic initiatives that foster engagement, provide valuable resources, and facilitate meaningful connections between alumni and current students. Examples include creating online platforms for networking and mentorship, organizing regular alumni events and workshops, and developing robust career services that leverage the expertise of alumni.
Investing in alumni relations professionals dedicated to building and maintaining strong alumni networks is crucial. These professionals can facilitate connections, manage communication channels, and develop programs that meet the evolving needs of alumni and current students. By fostering a culture of giving back, universities can encourage alumni to actively participate in mentoring and career guidance programs, further strengthening the network and improving career outcomes for future graduates.
Research Output and Innovation
A university’s commitment to research and innovation is a crucial factor influencing its overall standing and reputation. A strong research output, reflected in publications, patents, and the impact of that research on society, significantly contributes to a university’s global ranking. This section explores the research output of leading research universities and examines how universities cultivate environments conducive to research excellence.
The impact of research output on university rankings is multifaceted. High-impact publications in prestigious journals, numerous patents secured, and demonstrable societal impact from research all contribute to a higher ranking. Rankings often utilize metrics that quantify these outputs, weighing them against other factors like faculty quality and student outcomes. A university’s research reputation, built through consistent high-quality output, attracts top faculty and students, creating a virtuous cycle that further enhances its standing.
Research Output of Leading Research Universities
Examining the research output of several leading research universities provides a clearer picture of what constitutes a strong research profile. The following examples showcase the breadth and depth of research activity at these institutions.
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT): MIT consistently ranks highly in global university rankings, largely due to its prolific research output. Its researchers publish extensively in top-tier scientific journals, securing numerous patents in fields like engineering, computer science, and materials science. MIT’s research has led to significant advancements in various technological domains, contributing to its strong reputation for innovation. For instance, MIT’s Lincoln Laboratory has played a significant role in the development of radar and other defense technologies.
- Stanford University: Stanford University is another leading research institution with a substantial research portfolio. Its researchers are highly productive, publishing in diverse fields, including medicine, biotechnology, and artificial intelligence. Stanford’s strong ties to Silicon Valley have fostered a culture of entrepreneurship, leading to numerous spin-off companies based on research conducted at the university. A notable example is the development of Google’s PageRank algorithm, which originated from research conducted at Stanford.
- Harvard University: Harvard University boasts a diverse research landscape encompassing the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences. Its extensive research output is reflected in a large number of publications across a wide range of disciplines. Harvard’s researchers have made significant contributions to fields such as medicine, law, and economics, influencing policy and practice globally. The university’s extensive network of affiliated hospitals and research centers further strengthens its research capacity and impact.
Cultivating a Culture of Innovation and Research Excellence
Universities can actively foster a culture of innovation and research excellence through several key strategies. These strategies are essential for attracting top researchers, securing funding, and producing impactful research.
Providing adequate research funding, both through internal allocation and external grant acquisition, is crucial. Establishing collaborative research centers and institutes that bring together researchers from different disciplines can stimulate cross-fertilization of ideas and foster innovation. Furthermore, universities should prioritize mentorship programs and professional development opportunities to support early-career researchers and help them develop their research skills. Finally, fostering a supportive and inclusive research environment is essential for attracting and retaining top talent. This includes promoting diversity and inclusion among researchers and ensuring that all researchers have access to the resources and support they need to succeed.
Data Sources and Methodology: American University Ranking
Understanding the methodologies behind university rankings is crucial for interpreting their results effectively. Different ranking organizations employ varying data sources and weighting schemes, leading to diverse outcomes and potential biases. A critical analysis of these approaches is necessary to gain a comprehensive perspective on university performance.
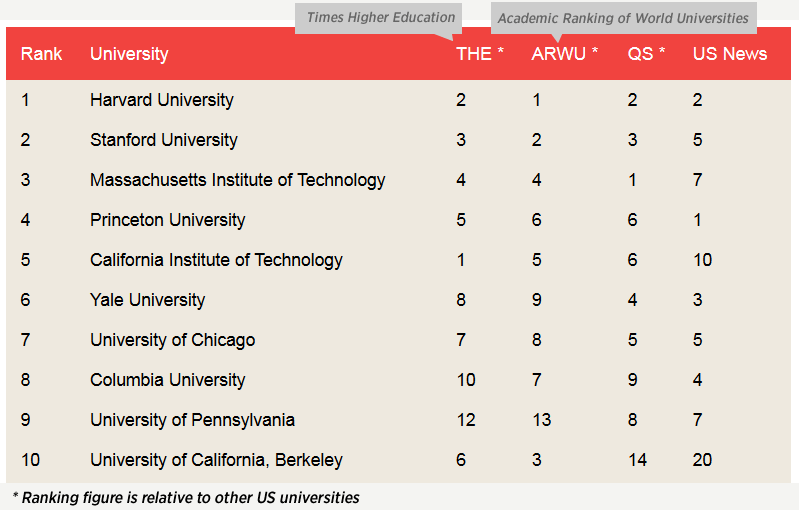
This section compares the data sources and methodologies of three prominent university ranking organizations: Times Higher Education (THE), QS World University Rankings, and U.S. News & World Report. We will examine their strengths and weaknesses, ultimately offering recommendations for enhancing the transparency and objectivity of university ranking systems.
Comparison of Data Sources and Methodologies
The three ranking systems utilize different data sources and weight them differently, resulting in varied rankings. A thorough understanding of these differences is essential for interpreting the results accurately.
- Times Higher Education (THE): THE utilizes 13 performance indicators across five areas: Teaching (30%), Research (30%), Citations (30%), Industry Income (2.5%), and International Outlook (7.5%). Their data sources include surveys, institutional data submissions, and bibliometric data from Elsevier’s Scopus database. They emphasize research output and international collaboration.
- QS World University Rankings: QS relies on six indicators: Academic Reputation (40%), Employer Reputation (10%), Faculty/Student Ratio (20%), Citations per Faculty (20%), International Faculty Ratio (5%), and International Student Ratio (5%). Their data primarily comes from global surveys of academics and employers, supplemented by institutional data. They place a strong emphasis on reputation and faculty-student ratios.
- U.S. News & World Report: U.S. News focuses specifically on US universities and uses a range of metrics, including peer assessment, graduation and retention rates, faculty resources, student selectivity, financial resources, and alumni giving. Their data comes from a combination of surveys, institutional data reports, and government sources. Their methodology is highly weighted towards factors related to selectivity and reputation.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Ranking Systems
Each ranking system possesses inherent strengths and limitations. A balanced assessment is needed to understand their value and limitations.
- Times Higher Education (THE): Strengths include a broad range of indicators, a focus on research output, and the use of a reputable bibliometric database. Weaknesses include potential biases in the citation data and a less direct measure of teaching quality.
- QS World University Rankings: Strengths include a global perspective and the incorporation of employer reputation, reflecting the employability of graduates. Weaknesses include a heavy reliance on reputation surveys, which can be susceptible to biases and subjective opinions. The relatively small weighting given to research output might not accurately reflect the research-intensive nature of some institutions.
- U.S. News & World Report: Strengths include a focus on factors relevant to undergraduate education in the US and a well-established reputation. Weaknesses include a heavy emphasis on selectivity, potentially overlooking institutions that serve diverse student populations or prioritize access over exclusivity. The reliance on self-reported data can also introduce inaccuracies.
Recommendations for Improving Transparency and Objectivity
To improve the transparency and objectivity of university rankings, several key changes are recommended.
- Increased Transparency in Methodology: Ranking organizations should provide more detailed explanations of their methodologies, including the specific weighting of each indicator and the sources of their data. This would allow for a more informed interpretation of the results.
- Diversification of Data Sources: Relying on a wider range of data sources, including student feedback, alumni outcomes data, and community engagement metrics, would provide a more holistic picture of university performance.
- Standardization of Data Collection: Implementing standardized data collection methods across institutions would minimize inconsistencies and improve the comparability of results. This might involve collaboration with governing bodies or professional organizations.
- Emphasis on Contextual Factors: Ranking systems should consider contextual factors, such as the institutional mission, student demographics, and resource availability, when evaluating universities. A “one-size-fits-all” approach is inadequate for comparing diverse institutions.
- Public Accountability and Peer Review: Ranking organizations should subject their methodologies to external peer review and make their data publicly available for scrutiny. This would enhance transparency and accountability.
Ultimately, understanding American university rankings requires a nuanced perspective. While numerical rankings provide a convenient snapshot, they shouldn’t be the sole determinant in choosing a university. Factors such as individual academic goals, preferred learning environment, financial considerations, and career aspirations must be carefully weighed against the available data. This guide has aimed to illuminate the multifaceted nature of these rankings, highlighting both their utility and limitations. By understanding the methodologies, biases, and the broader context, prospective students and others can make more informed decisions, ensuring a successful and fulfilling higher education experience.






